We pull back the curtains on how we build human-like voice capabilities at AI Rudder in four easy steps
Can AI Talk Like a Human?
Since the founding of AI Rudder, we have developed and completed more than a hundred product demonstrations for various clients all over the world.
From our experience, customers usually have a general understanding of what we do and the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) that we offer. A typical conversation over the phone would go something like this…
Customer: Cool! You guys build voice AI that talks to customers.
AI Rudder: Yes, we do!
Beyond the cool factor, what piqued the curiosity (or sometimes suspicion) for them is the science behind our technology.
Customer: But how does it work?
While most voice assistants today can only respond to simple questions in a somewhat robotic voice, our voice AI goes beyond to realistically replicate human interactions.
To help our customers make sense of and understand conversational AI, we will pull back the curtains on how we have built life-like voice capabilities in four easy steps.
Just like humans, voice AI creates a unique response in real-time for every question the customer poses. The response mainly depends on
- Who is the customer? Voice AI is backed up with a repository of customer data and insights like gender, job, age, etc.
- The context of the conversation, such as customer’s mood & intention from previous interaction (in the same call).
- Aim of the call. Voice AI calls the customer to achieve a specific objective, instead of open-ended conversations.
For example, Let’s say voice AI is going to call a customer named Jack, on behalf of an online car marketplace. The browsing history of Jack suggests that he is intending to buy a car. So the voice AI is used in this context to call Jack about buying a new car.
To start, we need to first understand who is the customer. Voice AI will elicit all relevant data about Jack from the database, where millions of customer data are stored (with consent).
Then a unique user profile of Jack is generated, as shown in the following image.

Based on the user profile of Jack, voice AI will have the following conversation with him:

To be more specific, let us take a closer look at how voice AI analyzed and responded to this particular sentence in the conversation:
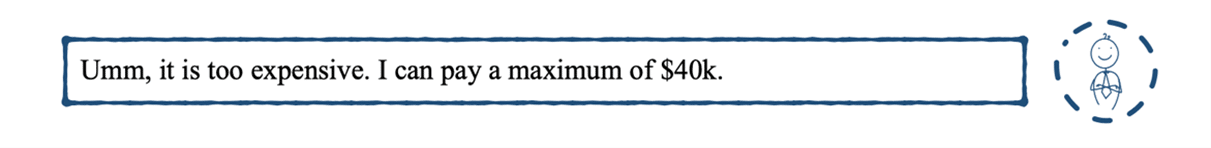
Four easy steps to how voice AI works:
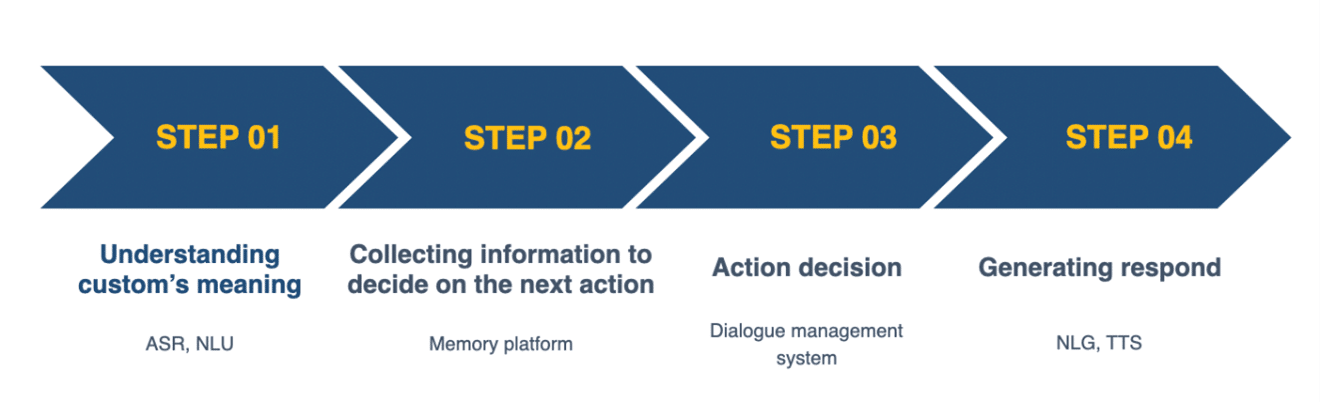
Step 1: Understanding customer’s meaning
First of all, voice AI tries to understand what Jack meant when he made the following statement.
By using a technology called ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition). AI can transcribe the voice response from Jack into text. More advanced ASR is also able to identify customers’ emotions by the tone of their voice.

Then the response in text form will be analyzed by a technology called NLU(Natural Language Understanding).
What NLU does is label the customer’s intention based on the text. There are over a hundred thousand labels in voice AI’s database, and AI will select one with the closest match.
For this sentence, AI labels it as “price too high”.
There is more to what NLU can do. For instance, it can also identify customers’ emotions based on the text. Further, it extracts important data points(slots) from sentences like figures, objects, etc, for future analysis. But to keep this explanation simple, we will skip these features for now.
Step 2: Collecting information to decide on the next action
Now that voice AI knows of Jack’s reaction to the price of the car. What does his response truly imply? Does he mean that the price tag is unacceptable, or is there a chance for him to accept the deal if we were to change the strategy?
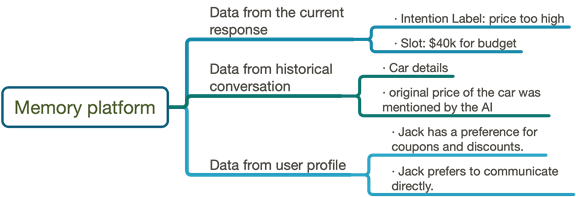
To decide on the next step to take, voice AI needs to gather and analyze all relevant information regarding the conversation. This not only includes the ASR and NLU results of the current words, but the historical dialogue and useful information from the customer’s profile.
A platform called memory platform will be gathering all the information, which can be seen in the following image.
Step 3: Action Decision
Aggregating all of the information from different sources, voice AI will come up with some possible outcomes:
- Jack is not uninterested in the car, he just thinks it is expensive. However, the price of the car is only slightly higher than his budget.
- We know that Jack likes to seek coupons and discounts for all kinds of purchases, and he likes to communicate in a direct manner.
Based on the information, Voice AI decides on the next course of action: continue selling the car to Jack. However, it will offer him a discount and free maintenance package, since that is what he likes.
Aside from that, voice AI will point out all these benefits directly and push for the deal, since Jack likes to communicate in a direct manner.
This whole decision-making process takes place in a so-called “dialogue management system”, where complex algorithms run after every response from the customer, to decide what to say next.
Step 4: Generating response
Based on the action decision outcome, voice AI generates the following response to Jack:

The technologies used here are NLG (Natural Language Generation) and TTS(Text to Speech).
By now, voice AI has completed one round of conversation with Jack.
For all the other rounds of the conversation in the call, the same workflow will be executed again and again. In this case, voice AI will speak to the customer continuously, to sell the car and close the deal.
In summary, our voice AI creates real-time responses for every interaction with the customer, combining the analysis of:
- Current feedback from the customer (ASR & NLU results).
- Historical conversation. Namely, what happened before (from the memory platform).
- The objective and purpose of the call, and customer profile from the database.


